Visitors have accessed this post 126 times.
Introduction:
In today’s world, our lungs are particularly vulnerable to various factors that can compromise their health. These include air pollution from vehicles and industrial emissions, smoking, and pre-existing lung conditions like asthma, bronchial asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). To ensure a healthy life, it is crucial to prioritize the purity and well-being of our lungs. This necessitates understanding how our lungs function.
Structure of the Lungs:
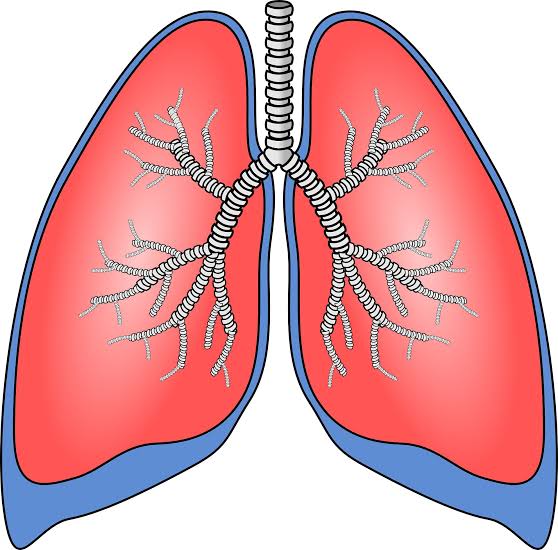
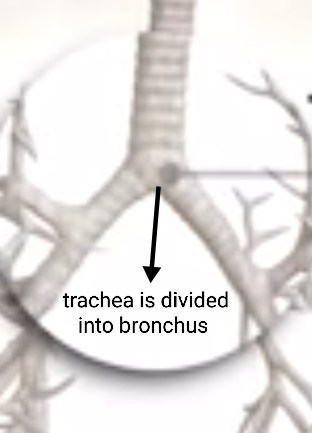
Unlike most internal organs that exist as singular entities, our body contains two lungs, along with two kidneys. The lungs, nestled safely in the chest cavity, share space with the heart. These are protected by the rib cage. The airway begins behind the nose in the form of the trachea, which then branches into bronchi.
Further branching leads to smaller bronchioles, which culminate in tiny sac-like structures known as alveoli. Surrounding the alveoli are blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, facilitating the exchange of gases.
Gas Exchange Process in a Single Breath:
When we inhale, air enters our nasal passage, where microscopic structures called cilia cleanse the inhaled air by removing dust particles. The air is then warmed and humidified before entering the trachea. From the trachea, the air passes through bronchi, bronchioles, and finally reaches the alveoli. The pulmonary arteries surrounding the alveoli extract the oxygen from the inhaled air, while impure blood from the heart releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the alveoli during exhalation. This gas exchange process enriches the blood with oxygen, which is then transported to the heart and subsequently distributed throughout the body. Achieving a complete breath relies on the coordinated action of the muscles in our nose, rib cage, and diaphragm.
Factors Affecting Lung Health:
Several activities and factors can significantly impact the health of our lungs, including:
1. Smoking: Inhaling cigarette smoke introduces toxic substances, such as nicotine, to our lungs. Nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream during gas exchange, spreading throughout the body. It stimulates the brain’s pleasure center, leading to addiction and affecting brain cells. Active smoking and passive smoking, which occurs when we inhale secondhand smoke, both contribute to the formation of black patches in the lungs, disrupting the gas exchange process.
2. Air Pollution: Industrial emissions and vehicular pollutants release harmful gases into the atmosphere. Our nose and lungs contain macrophages, which help eliminate smaller dust particles from inhaled air. However, these defense mechanisms have limitations, and prolonged exposure to pollutants can overwhelm their capacity.
3. Viral Infections: Viruses can spread through the air and enter our lungs when we come into close contact with infected individuals. If the viruses are highly virulent, our cilia and macrophages may be unable to clear them efficiently. Consequently, viruses can directly impact the lungs, leading to conditions like pneumonia and pleural effusion, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs.
Maintaining Healthy Lungs:
To keep our lungs healthy, the following tips can be beneficial:
1. Steam Therapy: Steam inhalation can help clear nasal congestion and provide relief. However, it should not be overdone and is recommended only when necessary, such as during nasal blockages.
2. Controlled Coughing: Controlled coughing techniques can aid in expelling phlegm and throat infections. Sitting comfortably with relaxed shoulders and feet flat on the floor, fold your hands over your stomach. Cover your mouth with a cloth or tissue, then cough two to three times in a controlled manner to clear the airway.
3. Postural drainage: It is an effective technique that aids in clearing the airways. When allergies, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) cause the bronchioles (tree-like structures) to constrict, mucus production increases to combat infections.
This excess mucus accumulates in the bronchial tubes, leading to breathlessness and difficulty in breathing. By practicing postural drainage, individuals can lie down or stand in positions that facilitate optimal air circulation. For instance, lying on either side with pillows positioned to angle the chest downward and the hips upward promotes the drainage of mucus from the bronchial tubes.
Physical activity :
Another crucial aspect of maintaining healthy lungs is engaging in physical activity and exercise. Regular exercise enhances lung capacity, allowing the body to intake more oxygen. Furthermore, physical activity promotes increased blood circulation, facilitating the expulsion of carbon dioxide from the body. By incorporating exercise into our daily routines, we can significantly improve our lung function and overall respiratory health.
Antioxidants:
The consumption of antioxidants is another key factor in supporting lung health. Green tea, in particular, is rich in antioxidants and possesses anti-inflammatory properties that bolster the immune system’s response to infections. Drinking green tea once or twice a day can provide substantial benefits to lung health. Additionally, certain foods such as turmeric, nuts (especially walnuts), cherries, blueberries, and green vegetables like beans and lentils are abundant in antioxidants and boost immunity.
Breathing patterns :
Developing proper breathing patterns is crucial for maintaining optimal lung function. The ideal ratio for inhalation to exhalation is 1:2. This means that for every inhalation, there should be twice the duration for exhalation. For example, if you inhale for five seconds, you should exhale for ten seconds. There are two primary techniques for achieving this. The first is pursed lip breathing, wherein inhalation is done slowly, and exhalation is performed with pursed lips, mimicking the act of blowing a whistle. The second technique is belly breathing, which involves observing the movement of the abdomen while breathing. By placing a hand on the belly while sitting, one can feel the stomach expand during inhalation and contract during exhalation.
Conclusion:
- It is crucial to prioritize lung health by adopting practices such as postural drainage, engaging in physical activity, consuming antioxidant-rich foods like green tea, turmeric, nuts, cherries, blueberries, and green vegetables, and developing proper breathing patterns. As the world evolves and pollution levels increase, it is even more critical to protect and care for our lungs, as they are vital to our overall well-being. By taking these proactive measures, we can ensure healthier lives and promote a brighter future for ourselves and future generations.